Contents:
Embarking on your journey as a tutor is a rewarding experience that allows you to impart knowledge and inspire others. However, as you begin to accumulate tutoring hours, it’s essential not to neglect the less thrilling but equally important aspect of being a self-employed tutor – managing your taxes.
It’s essential to be aware of and fulfil your tax responsibilities to HM Revenue & Customs (HMRC). If you work as a tutor on an online tutoring platform, such as PMT Education’s Tutoring Platform, you are not an employee but an independent contractor. This status means you’re responsible for managing your taxes, and failing to do so could result in significant penalties. Understanding your tax obligations is key to staying compliant and maximising your financial well-being. This guide aims to offer comprehensive insights into managing your taxes effectively, including how to submit your Self Assessment tax return.
Understanding your tax obligations
When you embark on self-employment as a tutor, you essentially become a ‘business owner’ in the eyes of HMRC. This status requires you to:
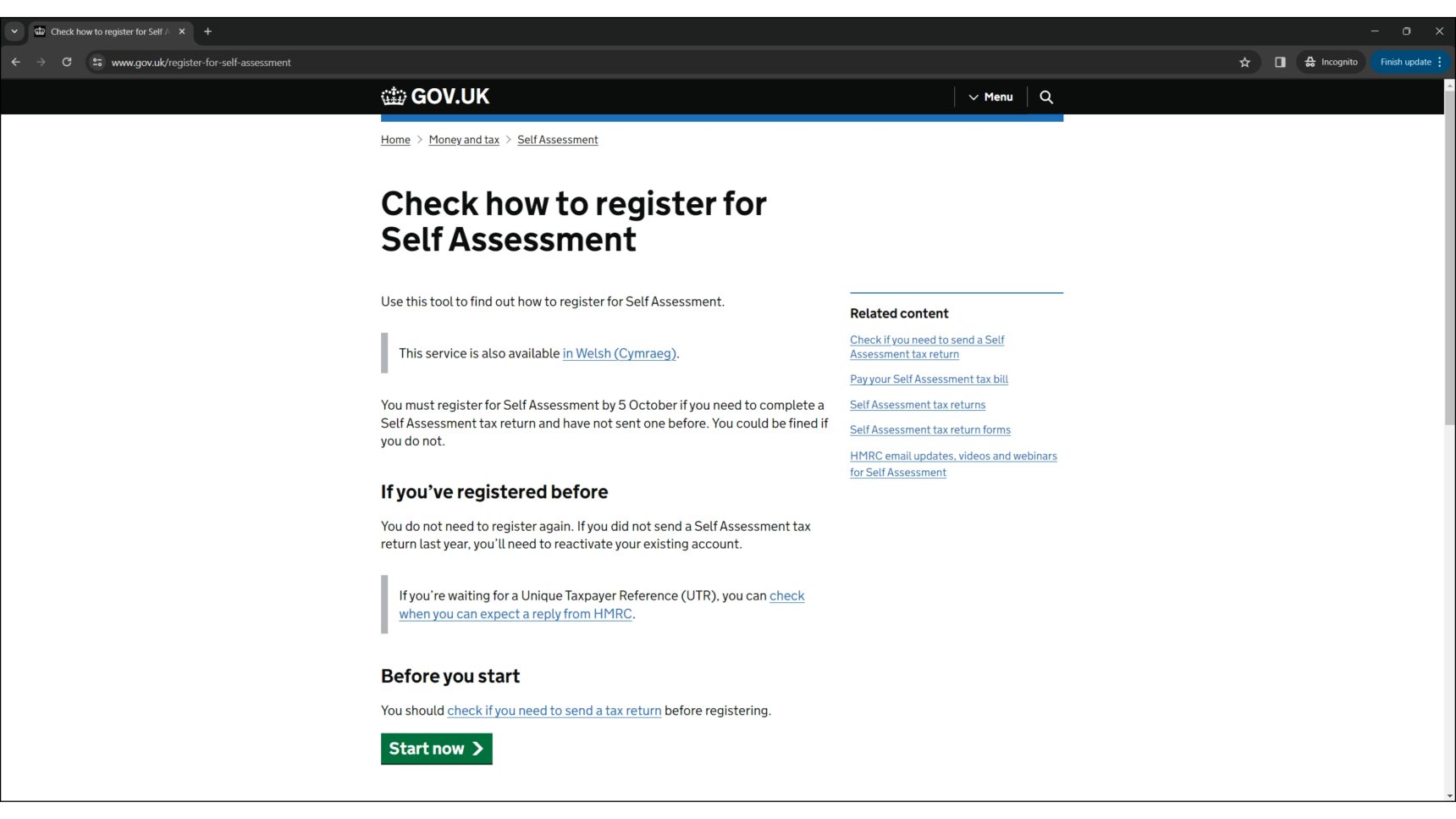
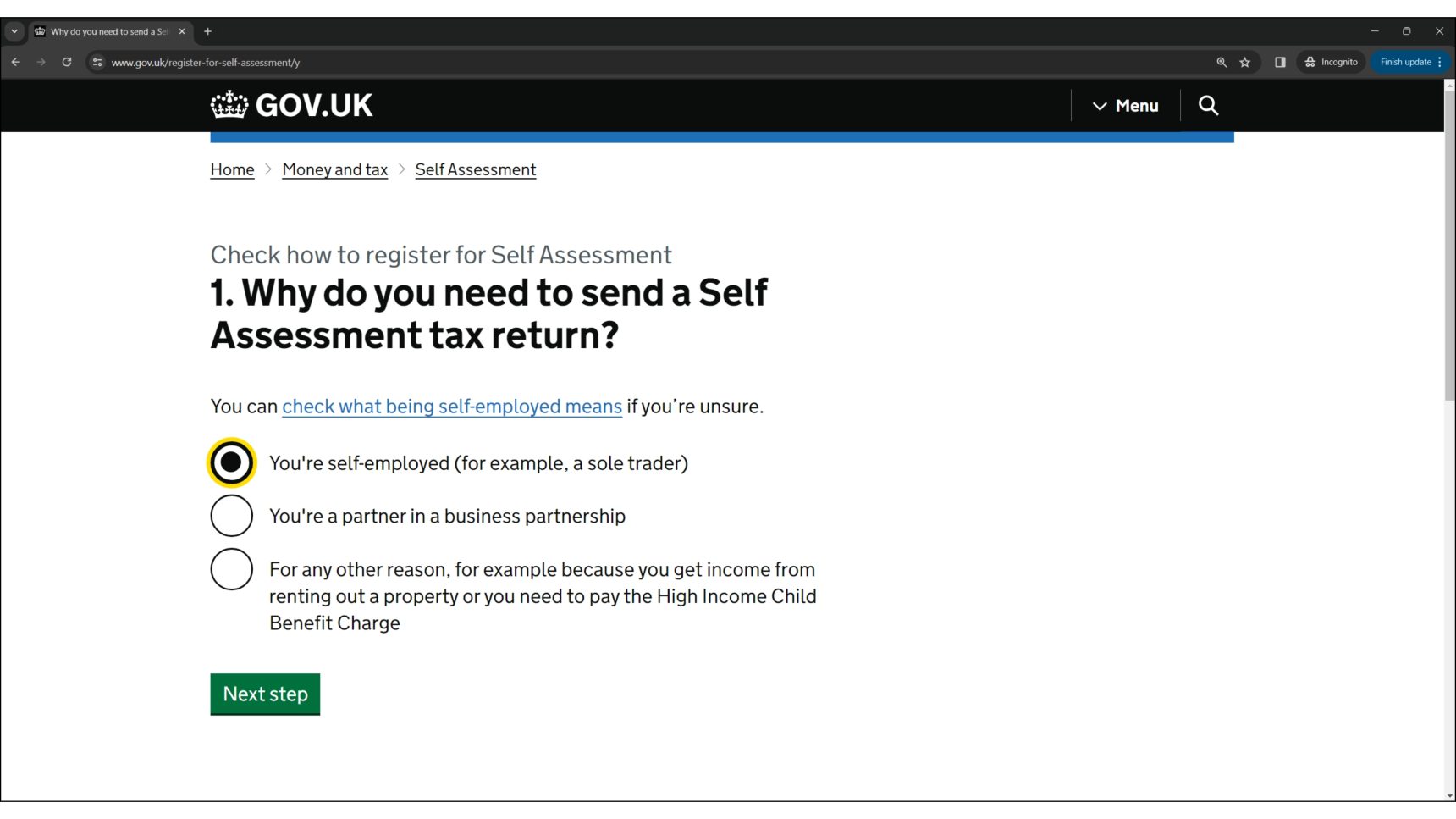
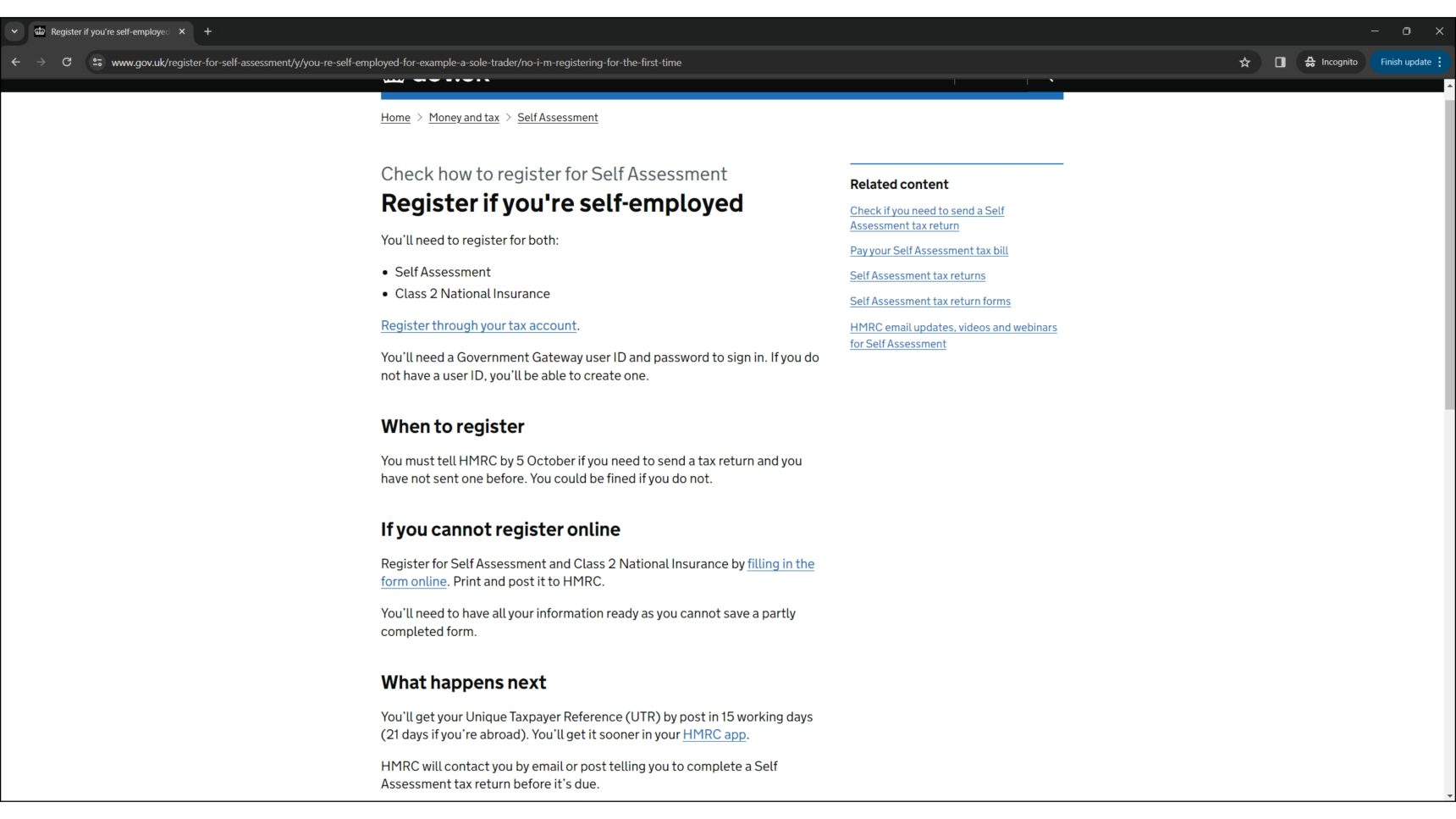
- Register for Self Assessment: If you have not sent a tax return before, it is likely that you will need to register with HMRC for Self Assessment. This is the system HMRC uses to collect Income Tax. You can use the Government’s online tool to check if you need to register for Self Assessment.
- Keep accurate financial records: It’s imperative to maintain detailed records of all your tutoring income and any expenses. I use an Excel spreadsheet to track my income. You can create a new row for each payment that you receive, whether it is from your clients or tutoring agency. If you have an accountant, you will need to provide them with this information when they file your tax return.
- Submit an annual tax return: You need to report your earnings and expenses annually by submitting a Self Assessment tax return. I use an accountant to file my tax returns to ensure they are filed correctly – any mistakes can cause you a hefty fine. A reputable accountant will charge roughly £300 for this service.
- Pay Income Tax and National Insurance contributions: Based on your profits, you may need to pay Income Tax and Class 2 and Class 4 National Insurance contributions. You must do this yourself and HMRC will communicate how to pay them. I find the HMRC mobile app makes this step very easy! You can download it on the App Store or Google Play.

When to register and submit a tax return
- Registration deadline: You must register by October 5th in your business’s second tax year. For instance, if you start tutoring in June 2023, you should register by October 5th 2024.
- Submission deadlines: The tax year runs from April 6th to April 5th. To avoid a penalty charge of £100, you must submit your tax return by January 31st following the end of the tax year. For the 2023/24 tax year, your online submission deadline is January 31st 2025.
- Payment deadlines: The same January 31st deadline applies for paying the tax you owe. There’s also a payment on account system, where you might need to make payments towards the next year’s tax bill on January 31st and July 31st.
For the 2023/2024 tax year, the Personal Tax Allowance is £12,570. If your earnings are below this threshold, you will not usually have to pay income tax. However, if your income exceeds £1000 in any given tax year, you must still file a tax return.
Tutor tax return setup guide
After setting up a Government Gateway account, you can log in to register for HMRC’s online services. HMRC will then mail your Unique Taxpayer Reference (UTR) number, which typically arrives within 10 working days. With your UTR number in hand, you’re ready to sign up for Self Assessment, prompting HMRC to send an activation code for your UTR by post, usually within a week. Upon receiving this code, you can activate your account and gain full access to the Self Assessment portal.
Organising your finances as a tutor
- Record-keeping: Keep records of all your tutoring income and related expenses. This can include receipts, invoices, bank statements, and mileage logs if you travel to clients.
- Understand deductible expenses: You can reduce your taxable income by deducting allowable expenses, such as advertising, office supplies, travel expenses directly related to tutoring, and a portion of your home expenses if you work from home.
- Separate bank account: Consider using a separate bank account for your tutoring business to simplify record-keeping.
Key tax tips for tutors
- Plan for tax payments: Set aside a portion of your income regularly to cover your tax bill. A good rule of thumb is to save 25-30% of your income.
- Stay informed: Tax laws and rates can change. Keep well-informed of any updates from HMRC that may affect your tax obligations.
- Use HMRC’s tools and resources: HMRC offers various tools, webinars, and guidance documents to help you understand and meet your tax responsibilities, as well as a really good mobile application.
- Consider professional help: If your financial situation is complex, consulting with an accountant can provide personalised advice and ensure you’re compliant while maximising your deductions.

Frequently asked questions
Do I have to declare employment income in my Self Assessment tax return?
You must disclose all sources of income, including your employment income and any other earnings, on your Self Assessment tax return to ensure you pay the correct amount of tax.
As a tutor, can I claim expenses for using my home as an office?
Yes, if you use part of your home for tutoring, you can claim a proportion of costs such as heating, electricity, Council Tax, mortgage interest, or rent.
How do I make payments on account?
Payments on account are essentially advance contributions to your upcoming tax bill, calculated from your tax liability in the previous year. These payments are split into two due dates: January 31st and July 31st. Indeed, this means you’re paying a portion of your next year’s tax bill ahead of time. It’s crucial to budget for these payments to avoid any financial surprises.
As a self-employed tutor in the UK, it is important to understand your obligations to HMRC for taxes. This includes registering for Self Assessment, maintaining accurate financial records, submitting annual tax returns, and making timely tax payments. By organising your finances, understanding deductible expenses, and planning for your tax payments, you can ensure compliance and optimise your financial wellbeing. Remember, while this guide provides a foundational understanding, tax regulations are subject to change, and seeking professional advice may be beneficial for complex situations.
While I have experience in submitting numerous tax returns myself, it’s important to clarify that I am not a certified accountant. The information provided here is intended as general advice. For comprehensive guidance or in situations that are more complex, it’s advisable to seek the expertise of a professional tax advisor.







Comments