Contents:
Our article on the benefits of pursuing a career in STEM highlighted the wide range of opportunities available and how new roles continue to emerge as research advances. But what exactly are these STEM career opportunities, and how can you narrow down your options? What pathways are available for entering the STEM field, and what qualifications are needed? In this article, we’ll guide you in choosing the right path into STEM and help you find the career that suits you best.
Navigating your path to a STEM Career
Whether you’re just finishing school or university, or are considering a career change, there are numerous ways to enter a career in STEM. The different pathways cater to a range of interests, priorities, and educational backgrounds. While many STEM disciplines traditionally require a university degree, it’s not the only option. Alternative degrees and work-based training are becoming increasingly popular, particularly in tech and engineering roles.
To help you decide which path is right for you, we’ve created detailed articles on each available pathway:
Accessing STEM careers through university
- Bachelor’s or integrated master’s: For school leavers who want to study STEM further before starting work, often including an optional foundation year or placement year
- Graduate entry job: For university graduates who already know their STEM career of interest
- Master’s or PhD: For university graduates who want to study further before entering the workforce
- Conversion course into STEM: For university graduates with a non-STEM bachelor’s degree who wish to transition into a STEM field
- Sponsored degree: For secondary school graduates who want to reduce the cost of studying STEM while securing a job for after graduation

Accessing STEM careers through alternative routes
- Direct from secondary school to entry-level job: For secondary graduates who want to start paid STEM work straight away
- Degree apprenticeship: For secondary school graduates who want to study STEM for free while gaining practical work experience
- Diploma courses: Short qualifications for students at various stages in their STEM education who have a clear career interest
- Online STEM certification courses: For individuals seeking accreditation for their knowledge in a specific area of STEM through online learning
- Coding bootcamps: Intensive, short-term programmes for those wanting to quickly acquire coding skills and enter the tech industry
- School leaver programmes: For secondary graduates who want to start paid STEM work in an environment tailored to beginners, with support and training
Identifying your interests and skills
The first step towards a STEM career is figuring out which STEM roles are best suited to you. Do you find yourself fascinated by how things work, a common trait among those interested in engineering? Or are you more inclined towards problem-solving and numbers, making mathematical roles more appealing? Identifying both your strengths and weaknesses is essential for determining the STEM careers in which you will thrive.
Take some time to reflect on your past experiences, hobbies, and subjects that excite you. If you’re still uncertain, consider taking aptitude tests or careers counselling focused on STEM. This self-assessment will help you choose the right path and maximise your chance of long-term job satisfaction. For additional guidance, you can explore the common strengths required for each STEM discipline in the image below.
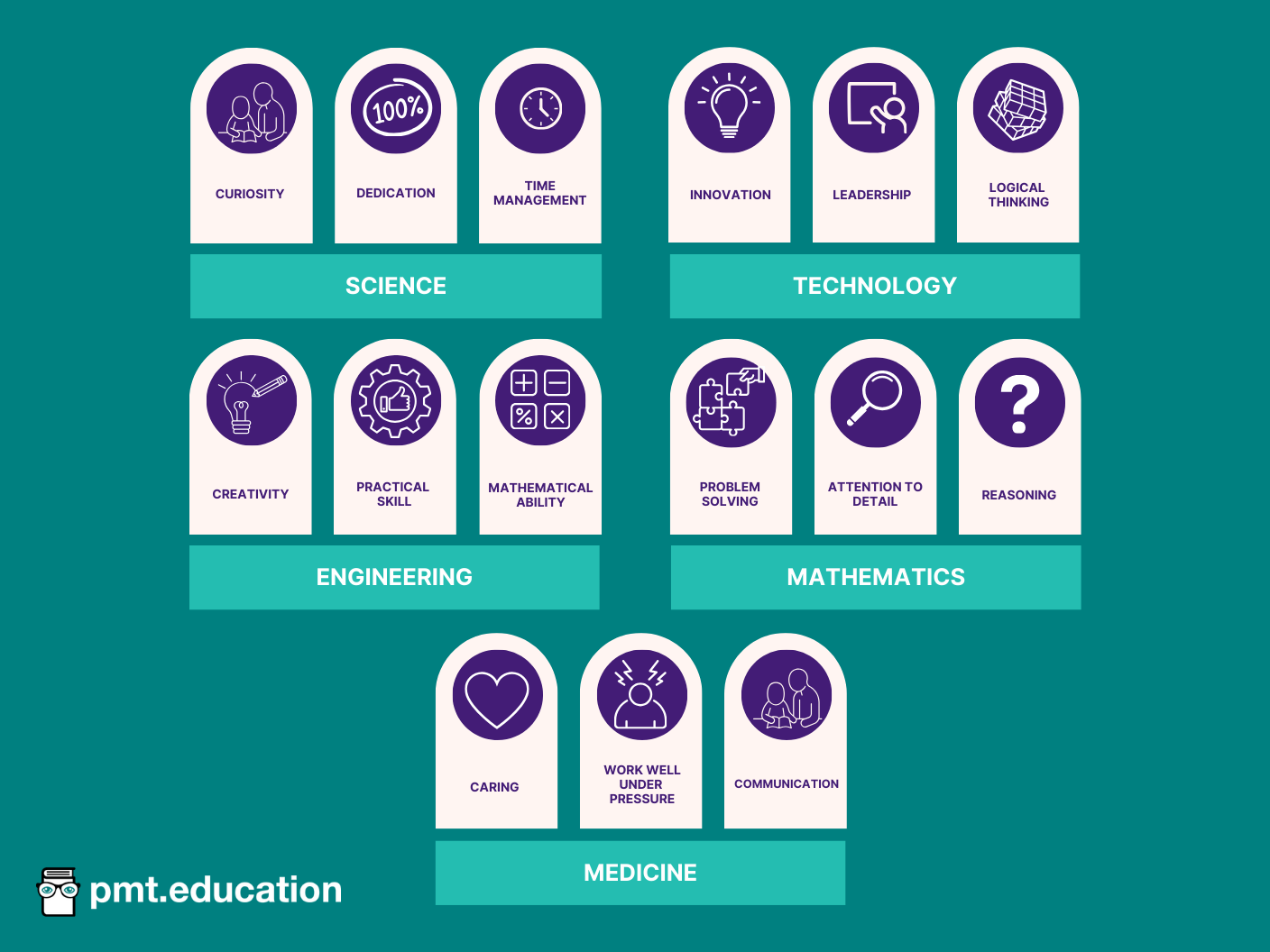
With a clear understanding of your interests and an awareness of your strengths and weaknesses, you can start exploring the available STEM career opportunities and narrow down your options.
Utilising available resources
Once you have completed your STEM education and are nearing the start of your STEM career, it’s time to begin job hunting. This involves reviewing lists of STEM job opportunities and narrowing down your options based on personal criteria that reflect your interests, strengths, and priorities. Additionally, make sure your criteria include the job’s qualification requirements to ensure they align with the STEM education pathway you have followed.
STEM job criteria checklist
- Select the STEM field you are most interested in.
- Write down your skills and match them with those in the job descriptions.
- Write down your weaknesses and look for roles with support and training opportunities available in the areas you want to improve. Certain companies will offer on-the-job training or mentorship to encourage your professional development.
- See which job descriptions give you excitement for the role.
- Look at job satisfaction reports. Previous and current employees will share their experiences of a company on sites such as GlassDoors. This can help you get a feel for a company before applying.
- Set a salary expectation. It’s likely you will be asked for your salary expectation in an interview and having an idea of what you need to earn for your lifestyle will help you to narrow your options.
- Select locations. Determine where you would be willing to relocate to, if at all, and use these parameters to narrow your STEM jobs list.
The STEM jobs list below shows some examples of career opportunities across science, technology, engineering, maths, and medicine.
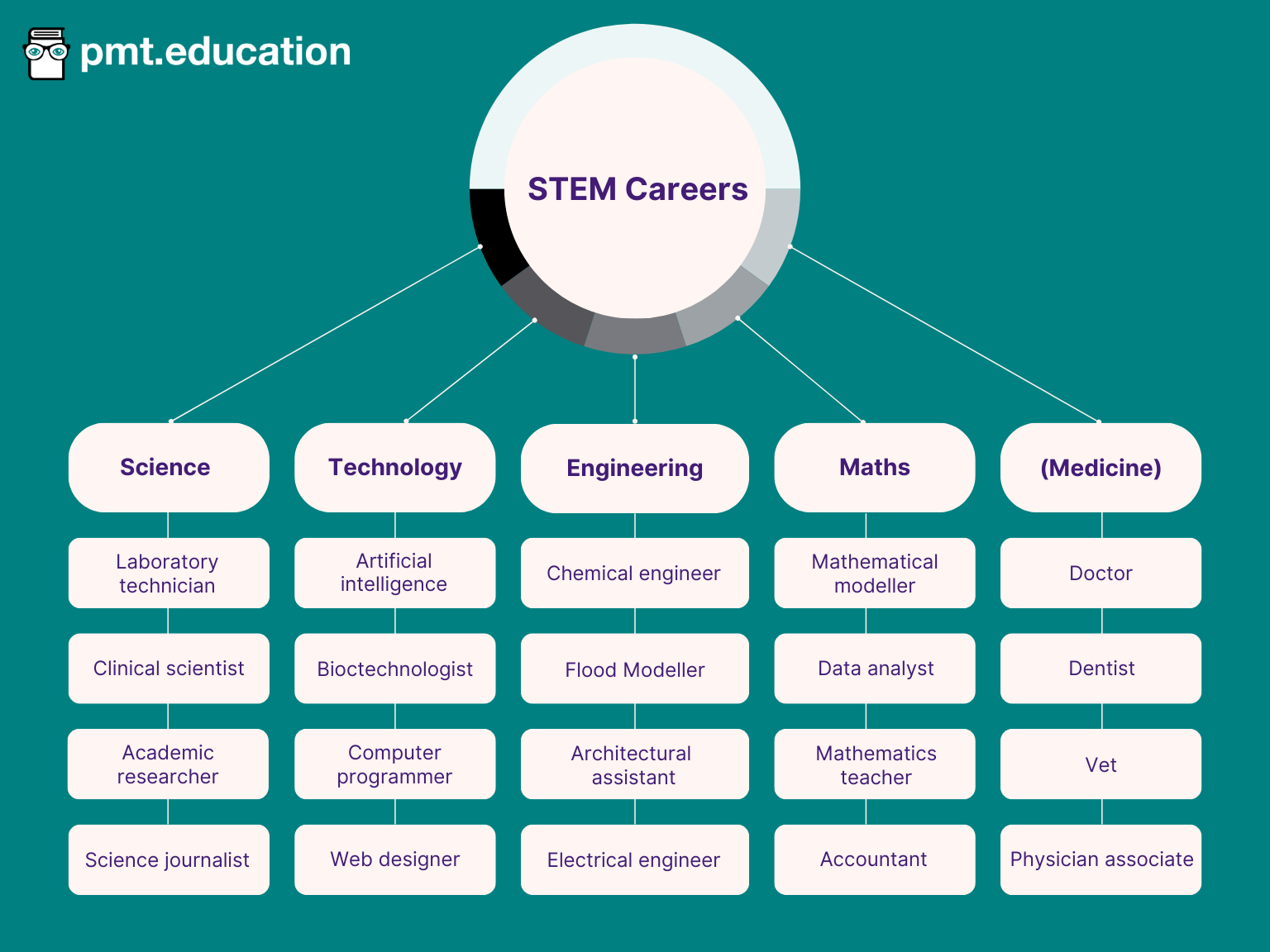
To access more expansive STEM jobs lists and further explore your career opportunities, there are lots of online resources available:
- Job boards: Use websites like Gradcracker for graduate roles, Youth Employment for entry-level STEM roles, All About School Leavers for school leaver programmes, and the New Scientist jobs website for general opportunities. These platforms allow you to filter the job listings by criteria such as location, industry, and qualification level.
- Recruitment agencies: Specialised STEM agencies work closely with companies seeking candidates with specific skills and educational backgrounds. By registering with these agencies, you can gain access to exclusive job openings tailored to your qualifications.
- University career services: If you’re a student or recent graduate, your university’s career services are an excellent resource. They often have extensive lists of STEM jobs, accumulated over years of assisting students in finding graduate roles. They also host career fairs, offer internship opportunities, and provide support in refining your CV and cover letter.
- Professional associations: Joining a professional association in your chosen field can open up networking opportunities and provide access to industry-specific job boards. Many associations offer student memberships, making it a great starting point for building your career network.
Networking and building connections
Networking involves engaging in conversations, making connections, and forming relationships with other professionals in your chosen STEM field. It’s a key aspect of the STEM job market, as colleagues and contacts can introduce new opportunities, offer guidance, and answer questions you may have before starting a STEM career. In fact, around 60% of jobs are never advertised publicly, as they are filled through networking. To access these unlisted roles, you’ll need to actively network – but how do you go about networking in STEM?
There are many ways to network. In-person networking can take place at career events, where you can engage with employees from companies that interest you, or through mentoring relationships with STEM professionals. Online networking can involve joining STEM groups and forums that share advice related to your field of interest, or reaching out directly to individuals in roles you’re aspiring to. One of the most popular platforms for online networking is LinkedIn.

How to effectively use LinkedIn
LinkedIn is an invaluable resource for job seekers. Many professionals maintain a profile on the platform, using it to collaborate, provide advice to job seekers, or share insights about their roles. By joining relevant groups and staying updated on industry trends, you can also appear well-prepared during interviews. Since LinkedIn is often the first place employers check when reviewing applications, it’s essential to use it effectively:
- Create a strong profile: Make sure your LinkedIn profile is complete and up-to-date. Highlight your education, skills, and experiences that are most relevant to the STEM jobs you’re pursuing.
- Have a professional profile photo: Your profile photo is the first impression people will get. A well-lit, professional photo increases your profile’s appeal and your chances of being contacted.
- Engage with content: Follow companies and industry leaders in your field. Engage with their posts by liking, commenting, and sharing to increase your visibility and demonstrate your interest in the industry.
- Connect with professionals: Don’t hesitate to reach out to professionals for advice or informational interviews. Most are willing to help if approached respectfully.
- Use the ‘Open to Work’ feature: Enable this setting to let recruiters know you’re looking for opportunities. Be specific about the roles you’re interested in to attract relevant job offers.
You can find examples of effective LinkedIn profile summaries that can enhance your LinkedIn experience and maximise your networking opportunities.
No matter what path you take, starting your career in STEM will be a journey that requires planning and dedication. Read the next article in this guide to learn how to effectively navigate the job application process.



Comments